To Share is to Show You Care!
In the ever-evolving landscape of artificial intelligence, the lack of control over decision-making processes has become a significant concern for businesses and individuals alike. As AI algorithms become more sophisticated, finding ways to assert control and ensure ethical outcomes has become imperative. In this blog post, we will delve into the challenges posed by the lack of control in AI decision-making and explore viable solutions to address this issue.
1. Understanding the Challenge: Lack of Control in AI Decision-Making

Artificial intelligence systems are designed to learn and adapt based on data inputs, and this very adaptability can sometimes lead to unpredictable outcomes. The lack of transparency and interpretability in AI algorithms can make it challenging for stakeholders to understand, trust, and control the decisions made by these systems.
2. The Impact of Uncontrolled AI Decision-Making
2.1 Ethical Concerns

Uncontrolled AI decision-making can give rise to significant ethical concerns, primarily stemming from biases embedded in the training data. When the data used to train AI models contains biases, the system may inadvertently make decisions that discriminate against certain groups or individuals. For example, if historical data used for training exhibits gender or racial biases, the AI system may perpetuate and amplify these biases in its decisions.
Addressing ethical concerns involves implementing measures to identify and mitigate biases during the development and training phases. This may include diversifying training datasets, employing bias-detection algorithms, and continuously monitoring and adjusting the AI system to ensure fairness in decision outcomes.
2.2 Regulatory Compliance Issues
Uncontrolled AI decision-making poses challenges in meeting regulatory requirements, as regulatory frameworks often mandate transparency, fairness, and accountability in automated decision systems. Organizations using AI systems must demonstrate compliance with these standards, which becomes challenging when decision-making processes lack transparency.
To address regulatory compliance issues, it is essential to implement governance frameworks and adhere to ethical AI guidelines. This includes documenting the decision-making process, ensuring accountability, and providing regulators with the necessary insights into how AI systems arrive at their conclusions. Regular audits and assessments can also help ensure ongoing compliance with evolving regulatory standards.

2.3 Reputation Risks

The lack of control over AI decision-making introduces the risk of unintended consequences, which can harm an organization’s reputation. Negative outcomes, such as biased decisions or unforeseen errors, can erode trust among customers, stakeholders, and the public. This loss of trust can have lasting impacts on an organization’s brand image and market position.
Mitigating reputation risks involves proactive measures, including transparent communication about AI processes, addressing issues swiftly when they arise, and incorporating ethical considerations into the development lifecycle. By being transparent about the steps taken to address AI-related challenges, organizations can demonstrate a commitment to responsible AI practices and rebuild trust with their audiences.
In summary, understanding and addressing the ethical concerns, regulatory compliance issues, and reputation risks associated with uncontrolled AI decision-making are crucial for fostering trust, ensuring fairness, and safeguarding the reputation of organizations deploying AI systems.
3. Solutions to Regain Control in AI Decision-Making
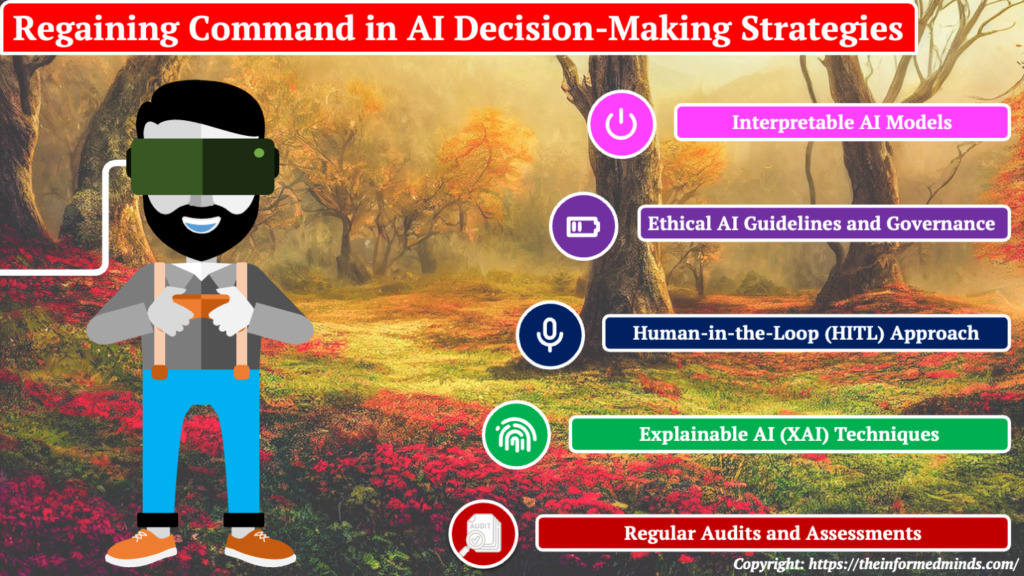
3.1 Interpretable AI Models
Interpretable AI models are designed to provide clear and understandable insights into how they make decisions. Unlike complex black-box models, interpretable models allow stakeholders to trace the decision-making process and understand the factors influencing each outcome. This transparency is crucial for gaining trust and confidence in AI systems. Techniques such as decision trees, rule-based models, and model-agnostic interpretability methods enable developers and users to interpret and validate AI decisions effectively.
3.2 Ethical AI Guidelines and Governance
Establishing ethical guidelines and governance frameworks for AI development and deployment is essential to ensure responsible and fair use of AI. Ethical guidelines provide a set of principles that guide developers in addressing biases, ensuring transparency, and prioritizing ethical considerations throughout the AI lifecycle. Governance frameworks encompass policies, procedures, and oversight mechanisms to enforce ethical guidelines and monitor compliance. This approach helps organizations align their AI initiatives with ethical standards and regulatory requirements.
3.3 Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) Approach
The Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) approach involves integrating human expertise into the decision-making loop of AI systems. This collaboration allows human experts to provide oversight, validation, and context to AI-generated decisions. By combining the strengths of AI automation with human judgment, organizations can strike a balance that mitigates the risk of biased or unintended outcomes. HITL ensures that decisions align with human values, ethical considerations, and domain-specific expertise.
3.4 Explainable AI (XAI) Techniques
Explainable AI (XAI) techniques focus on making AI models more transparent and understandable. These techniques provide insights into how a model arrives at a particular decision, offering explanations that can be comprehended by both technical and non-technical stakeholders. Methods such as feature importance analysis, attention mechanisms, and model-agnostic interpretability tools contribute to the development of AI systems that can be easily explained and validated.
3.5 Regular Audits and Assessments
Conducting regular audits and assessments of AI systems is crucial for identifying and addressing issues related to biases, fairness, and overall performance. Audits involve reviewing the training data, model architecture, and decision outcomes to ensure alignment with ethical guidelines and regulatory standards. Continuous monitoring and assessment allow organizations to adapt their AI systems to changing conditions, evolving data landscapes, and emerging ethical considerations, thus promoting ongoing improvement and responsible use of AI.
Conclusion
In the rapidly advancing field of artificial intelligence, regaining control over decision-making processes is paramount for fostering trust and ensuring ethical practices. By adopting interpretable models, establishing ethical guidelines, incorporating human oversight, and leveraging explainable AI techniques, organizations can navigate the challenges posed by the lack of control in AI decision-making. As we move forward, it is crucial for businesses and developers to stay proactive in addressing these challenges, thereby paving the way for responsible AI innovation and a more secure digital future.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What are the problems with AI decision-making?
A: AI decision-making faces challenges such as biases in training data, lack of transparency in complex models, and the potential for unintended consequences, leading to ethical concerns.
Q2: How does artificial intelligence affect management decision-making?
A: Artificial intelligence impacts management decision-making by providing data-driven insights, automating routine tasks, and improving efficiency. However, it also introduces challenges related to transparency, accountability, and the need for human oversight.
Q3: What are the problems with automated decision-making?
A: Automated decision-making can suffer from biases in training data, lack of interpretability, and the risk of making decisions based on incomplete or inaccurate information, raising concerns about fairness and accountability.
Q4: Can artificial intelligence take decisions independently?
A: Artificial intelligence can make decisions independently based on learned patterns and data. However, human oversight is crucial to ensure ethical and responsible decision-making, especially in complex or novel situations.
Q5: What is the most common problem in AI?
A: One of the most common problems in AI is biased decision-making, where models reflect and perpetuate biases present in the training data, leading to unfair outcomes.
Q6: What are the biggest challenges in AI?
A: The biggest challenges in AI include addressing biases, ensuring transparency, fostering interpretability, managing ethical considerations, and striking a balance between automation and human oversight.
Q7: How does intelligence affect decision-making?
A: Intelligence enhances decision-making by enabling the processing of information, learning from experience, and adapting to changing circumstances. In AI, intelligence contributes to the ability to make informed decisions based on data.
Q8: How does artificial intelligence affect management and leadership?
A: AI influences management and leadership by streamlining processes, providing data-driven insights, and automating routine tasks. However, it also requires leaders to navigate challenges related to ethical use, workforce impact, and decision accountability.
Q9: What is the impact of AI in human resource decision-making processes?
A: AI impacts human resource decision-making by automating tasks like resume screening and providing data-driven insights for recruitment. However, it raises concerns about biases and the need for a human touch in sensitive HR decisions.
Q10: What are the 3 conditions affecting decision-making?
A: The three conditions affecting decision-making are uncertainty, complexity, and ambiguity. These factors can pose challenges for both human and AI decision-makers.
Q11: What is one disadvantage to automating a decision-making process?
A: One disadvantage of automating a decision-making process is the potential for overlooking nuanced or context-specific factors that a human decision-maker might consider, leading to suboptimal outcomes.
Q12: What is the difference between AI and automated decision-making?
A: AI refers to the broader concept of machines simulating human intelligence, while automated decision-making specifically involves the use of algorithms and rules to make decisions without human intervention.
Q13: Who is responsible for decisions made by AI?
A: The responsibility for decisions made by AI lies with both the developers who design the algorithms and the organizations deploying the AI systems. Establishing clear ethical guidelines and governance structures is crucial for accountability.
Q14: What are decision rules in AI?
A: Decision rules in AI are predefined conditions and criteria that guide the decision-making process of algorithms. These rules help determine the output or action based on input data.
Q15: What are the pros and cons of artificial intelligence decision-making?
A: Pros of AI decision-making include efficiency, data-driven insights, and automation. Cons involve challenges such as biases, lack of transparency, ethical concerns, and the potential for job displacement. Balancing these factors is crucial for responsible AI decision-making.
The Informed Minds
I'm Vijay Kumar, a consultant with 20+ years of experience specializing in Home, Lifestyle, and Technology. From DIY and Home Improvement to Interior Design and Personal Finance, I've worked with diverse clients, offering tailored solutions to their needs. Through this blog, I share my expertise, providing valuable insights and practical advice for free. Together, let's make our homes better and embrace the latest in lifestyle and technology for a brighter future.